Overview
How the Regulation Was Introduced
What are Conflict Minerals?
Regardless of the origin of a conflict zone, 3TG and cobalt are called conflict minerals.
Conflict minerals (3TG) and cobalt
Tin, Tantalum, Tungsten, Gold, CobaltConflict Minerals Minerals (tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold) extracted from the conflict zones near Congo in central Africa
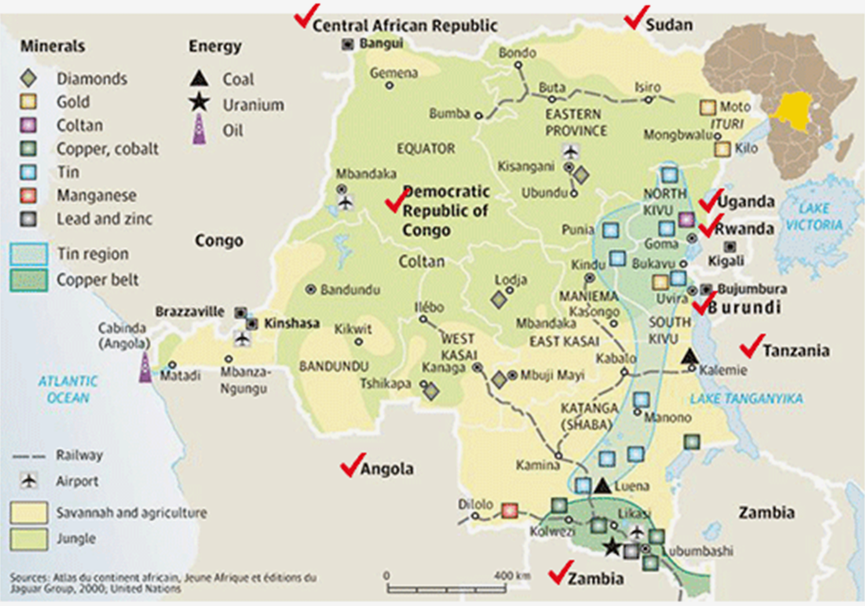
Ten conflict zones
DR of the Congo, South Sudan, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Zambia, Angola, Tanzania, and South Africa.What is Conflict Minerals Regulation? As part of economic sanctions to eradicate social problems such as human rights abuses, child labor exploitation, and sexual assaults committed in African conflict regions (10 countries including DR Congo), mainly developed countries designated the five minerals mined in these regions (3TG: Tin, Tungsten, tantalum, gold, and cobalt) as conflict minerals, and established this new regulation that restricts the use of conflict minerals by companies to prevent the inflow of money from mining operations to rebels as their military funds.
Rebels commit unethical social problems such as human rights violations, child labor exploitation/abuse, and sexual assaults while mining the minerals.
Mineral extraction proceeds flow to fund the rebels' military -- continuing the war.